The field of injection molding has been around for decades, allowing manufacturers to achieve incredible accuracy and consistency in the production of plastic parts. One of the most critical elements in achieving success in injection molding is understanding the differences between melting amorphous and semi-crystalline plastics.
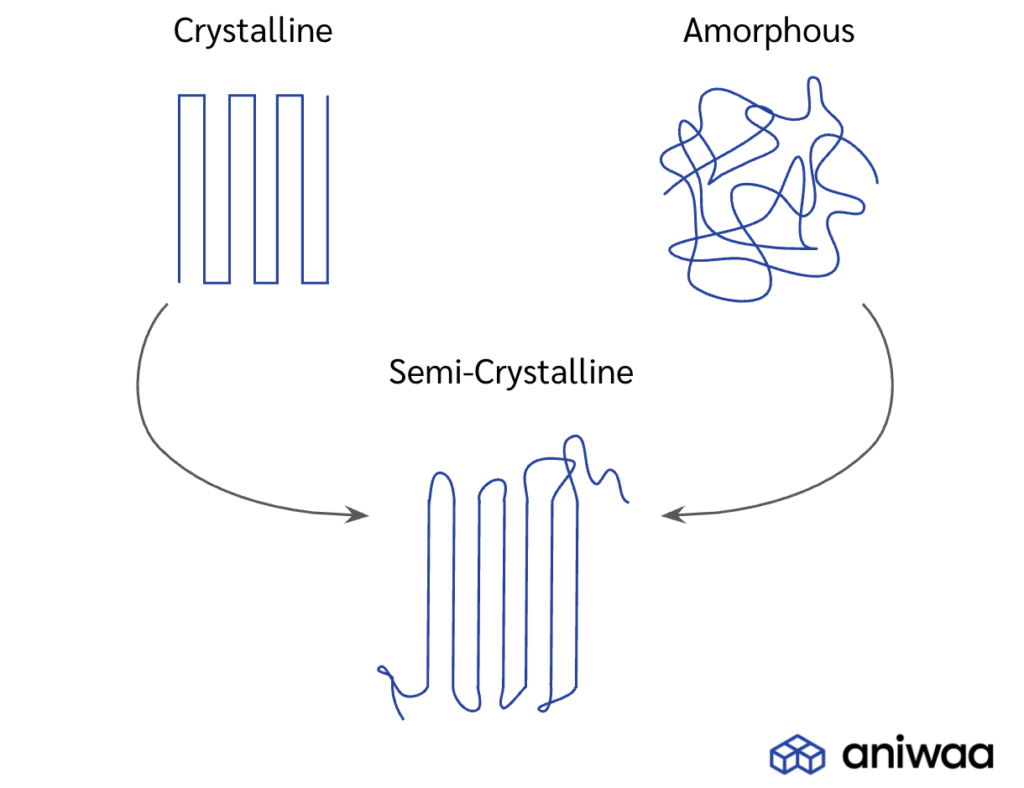
Amorphous plastics, such as polycarbonate, have a disordered molecular structure, resulting in no clear melting point. These plastics soften gradually as they heat, ultimately becoming a molten liquid. Semi-crystalline plastics, such as polypropylene, have a more ordered molecular structure, allowing them to melt at a specific temperature.
The challenge with melting amorphous plastics is achieving uniform melt viscosity throughout the mold. These plastics have a higher rate of thermal expansion and contraction, which can cause variation in viscosity, leading to differences in the part's final appearance and mechanical properties. In contrast, semi-crystalline plastics have a well-defined melting point, allowing for more uniform viscosity and consistent parts' production.
To achieve the desired uniformity in amorphous plastics, manufacturers sometimes use a technique called shear rate control. This technique involves adjusting the rate at which the plastic is injected into the mold, creating an even flow of material throughout the injection process. However, this technique is not always effective, and it is not suitable for all amorphous plastics.
Amorphous plastics also generally require higher injection pressures and longer cycle times than their semi-crystalline counterparts. They are also often more prone to warping and deformation, making it more challenging to achieve consistently high-quality parts.
On the other hand, semi-crystalline plastics make it easier to achieve high-quality parts with a shorter cycle time. However, these plastics are more sensitive to the cooling rate, meaning that the mold's cooling time must be precisely controlled to prevent deformation.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between amorphous and semi-crystalline plastics is critical for achieving success in injection molding. While amorphous plastics require more precise control of the melting and flow process, semi-crystalline plastics offer a more defined melting point, making them more consistent in production. Ultimately, it is up to manufacturers to determine which plastic they will use based on the specific part's requirements and the desired end result.
All-Star Plast, a leading plastic mold manufacturer in China, understands the complexities of injection molding and is equipped to handle both amorphous and semi-crystalline plastic production. With over 15 years of experience, their team of experts can provide the necessary support and guidance to help their clients achieve high-quality, consistent results.